Learn the differences between Modbus TCP vs Modbus RTU
ฝัง
- เผยแพร่เมื่อ 8 ก.ย. 2024
- Learn the differences between Modbus TCP vs Modbus RTU
Differences with respect to Network Models, OSI 7 layer communication stack and Frame Structure.
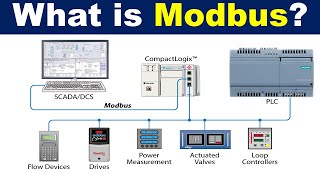
Modbus is a widely used communication protocol in industrial automation systems. The two common variants, Modbus TCP and Modbus RTU, have distinct differences in terms of communication methods, performance, and applications.
Modbus TCP
Communication Method: Utilizes Ethernet and TCP/IP for communication.
Protocol Layers: Operates at the application layer of the OSI model and uses TCP/IP at the transport layer.
Data Transmission: Supports higher data transfer rates due to the use of Ethernet.
Physical Medium: Uses standard Ethernet cables (Cat 5, Cat 6, etc.) and network hardware (switches, routers).
Network Topology: Allows for more complex network topologies, including star, ring, and mesh networks.
Addressing: Uses IP addresses for addressing devices, enabling easy integration with other networked systems.
Error Handling: Benefits from TCP's built-in error-checking and recovery mechanisms.
Ease of Integration: Easier to integrate with modern IT infrastructure and SCADA systems.
Device Count: Supports a large number of devices due to the scalability of Ethernet networks.
Modbus RTU
Communication Method: Utilizes serial communication (RS-232, RS-485) for data exchange.
Protocol Layers: Operates at the data link layer of the OSI model, using simpler frame structures compared to TCP/IP.
Data Transmission: Generally supports lower data transfer rates compared to Ethernet-based Modbus TCP.
Physical Medium: Uses serial cables (RS-232, RS-485) and requires specific hardware for serial communication.
Network Topology: Typically limited to point-to-point or multi-drop (daisy-chain) topologies.
Addressing: Uses a simple address field within the Modbus RTU frame for identifying devices, with a typical limit of 247 devices.
Error Handling: Includes basic error-checking mechanisms (CRC) but lacks the advanced recovery features of TCP.
Ease of Integration: May require additional hardware (e.g., serial-to-Ethernet converters) for integration with modern networks.
Device Count: Limited by the nature of serial communication, generally supporting fewer devices compared to Ethernet networks.
Summary
Modbus TCP is preferred for modern, large-scale, and high-speed applications where integration with IT infrastructure is important.
Modbus RTU is suitable for smaller, simpler systems with lower data transfer requirements, particularly in legacy installations or where Ethernet infrastructure is not available.
Applications
Modbus TCP: Often used in larger industrial environments, where devices need to be networked over long distances, and in systems requiring frequent and high-speed data exchanges.
Modbus RTU: Common in localized control systems, smaller industrial setups, and environments where robustness and simplicity of serial communication are advantageous.





![[UNCUT] The Loyal Pin ปิ่นภักดิ์ EP.6 (1/4)](http://i.ytimg.com/vi/m05kZ2GDKXg/mqdefault.jpg)

