Anhyd. AlCl3 in Organic Chemistry | Friedel Craft Alkylation and Acylation | Jee Main, Advanced NEET
ฝัง
- เผยแพร่เมื่อ 24 ก.ย. 2024
- Hello guys, In this lecture we are going to discuss the role of anhydrous AlCl3 in organic chemistry. Different cases of Friedel craft alkylation and acylation and other reactions with multiple cases has been discussed in details.
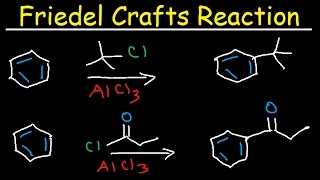
The Friedel-Crafts alkylation is an organic reaction used to convert an aryl compound and an alkyl halide to a substituted aromatic compound using a Lewis acid catalyst (such as AlCl3). The reaction begins with the Lewis acid abstracting the halide from the alkyl halide to form an electrophilic alkyl cation and a tetrasubstituted aluminum anion. The aromatic compound then attacks the alkyl cation via an electrophilic aromatic substitution (SEAr) to give a cationic product with loss of aromaticity. Deprotonation with the aluminum anion results in the final aromatic product and regeneration of the Lewis acid catalyst
This electrophilic aromatic substitution allows the synthesis of monoacylated products from the reaction between arenes and acyl chlorides or anhydrides. The products are deactivated, and do not undergo a second substitution. Normally, a stoichiometric amount of the Lewis acid catalyst is required, because both the substrate and the product form complexes.
The Friedel-Crafts Alkylation may give polyalkylated products, so the Friedel-Crafts Acylation is a valuable alternative. The acylated products may easily be converted to the corresponding alkanes via Clemmensen Reduction or Wolff-Kishner Reduction.
MECHANISM FOR THE FRIEDEL-CRAFTS ACYLATION OF BENZENE
Step 1:
The acyl halide reacts with the Lewis acid to form a complex.
Step 2: Loss of the halide to the Lewis acid forms the electrophilic acylium ion.
Step 3: The p electrons of the aromatic C=C act as a nucleophile, attacking the electrophilic C+. This step destroys the aromaticity giving the cyclohexadienyl cation intermediate.
Step 4: Removal of the proton from the sp3 C bearing the acyl- group reforms the C=C and the aromatic system, generating HCl and regenerating the active catalyst.
Many more concepts and examples has been dealt in details inside the lecture.
Some other very useful lectures:-
Sodium Borohydride in Organic Chemistry | NaBh4 Details| Explained by IITian | Mains, Advanced| NEET
• Sodium Borohydride in ...
LiAlH4 in One Shot | Concept Booster | Explained by IITian | Mains, Advanced | NEET | AIIMS
• LiAlH4 in One Shot | C...
DIBAL-H in Organic Chemistry || Explained by IITian || Jee Mains | Advance | NEET | AIIMS
• DIBAL-H in Organic Che...
Thanks for Watching.
Keep Sharing, Keep Supporting!!!