The Integumentary System: Understanding Skin Physiology
ฝัง
- เผยแพร่เมื่อ 29 ก.ย. 2024
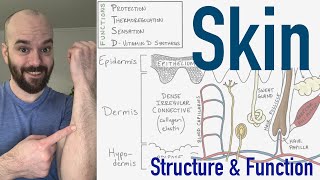
- The skin is the largest organ of your body. It is part of the integumentary system which, along with skin, is composed of hair follicles, melanocytes, nerves, fat, blood vessels, and lymph vessels. The integumentary system’s most important function is protection. It protects your insides from the outside. Melanin is a barrier against UV rays, and skin is waterproof, so you can go for a swim without swelling up like a grape. The integumentary layer is composed of three parts, from outermost to innermost: the epidermis, the dermis, and the hypodermis. The epidermis is mainly composed of epithelial cells. The dermis contains connective tissues, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, immune cells, nerves, and hair follicles. The hypodermis contains subcutaneous fat.
#skin #anatomy #organ
References:
openstax.org/b...
www.ncbi.nlm.n...
doi.org/10.101...
Image credits:
commons.wikime...
commons.wikime...
commons.wikime...
www.shuttersto...
If you wish to buy/license this video, please write to us at admin@scienceabc.com.
Voice Over Artist: John Staughton ( www.fiverr.com... )
SUBSCRIBE to get more such science videos!
/ @scienceabc
Follow us on Twitter!
/ abc_science
Follow us on Facebook!
/ sciabc
Follow us on Instagram!
/ scienceabcofficial
Follow us on LinkedIn!
/ scienceabc
Follow our Website!
www.scienceabc...





![[TH] FS vs BME - VCT Ascension Pacific - Lower Bracket Final](http://i.ytimg.com/vi/wnygqsR2Fig/mqdefault.jpg)


Spiderman is so lucky! he only has 11 months 'til Christmas. He lost May.
Excellent summary. Thanks!
Glad you liked it 😊
This animation really helps me understand a lot!
We're glad it helped!
Excellent explanation and thankyou for the mnemonic
Glad it was helpful!
I really like to way you explain.
perfect
Brilliant!!
Glad you liked it! :)
### Integumentary System Overview
The integumentary system consists of the skin and its appendages, including hair, nails, and glands. It has several key functions: protection, sensation, thermoregulation, excretion, vitamin D synthesis, and water resistance.
### Layers of the Skin
1. **Epidermis**: The outermost layer, composed mainly of keratinocytes.
- **Stratum Corneum**: Dead keratinized cells providing a barrier.
- **Stratum Lucidum**: Present only in thick skin (palms, soles).
- **Stratum Granulosum**: Cells begin to die and keratinize.
- **Stratum Spinosum**: Provides strength and flexibility.
- **Stratum Basale**: Deepest layer where cell division occurs.
2. **Dermis**: The middle layer, containing blood vessels, nerves, and glands.
- **Papillary Layer**: Loose connective tissue, forming dermal papillae.
- **Reticular Layer**: Dense connective tissue, providing strength and elasticity.
3. **Hypodermis (Subcutaneous Layer)**: Deepest layer, composed of adipose tissue for insulation and cushioning.
### Functions of the Integumentary System
1. **Protection**: Barrier against physical damage, UV radiation, and pathogens.
2. **Sensation**: Nerve endings detect touch, temperature, pain, and pressure.
3. **Thermoregulation**: Sweat production and blood vessel regulation maintain body temperature.
4. **Excretion**: Sweat removes waste products.
5. **Vitamin D Synthesis**: UV radiation converts cholesterol to vitamin D.
6. **Water Resistance**: Prevents dehydration by controlling water loss.
### Accessory Structures
1. **Hair**: Provides protection, sensory input, and regulates temperature.
2. **Nails**: Protect tips of fingers and toes.
3. **Glands**:
- **Sebaceous Glands**: Secrete sebum to lubricate skin and hair.
- **Sudoriferous (Sweat) Glands**:
- **Eccrine Glands**: Produce sweat for cooling.
- **Apocrine Glands**: Found in armpits and groin, produce thicker sweat.
### Common Skin Conditions
1. **Acne**: Inflammation due to blocked sebaceous glands.
2. **Eczema**: Red, itchy, and inflamed skin.
3. **Psoriasis**: Overproduction of skin cells leading to scaling.
4. **Skin Cancer**: Includes basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
### Visual Aid
Imagine a cross-sectional diagram of the skin with layers (epidermis, dermis, hypodermis) and structures (hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands) labeled. This can help visualize the system's components and their functions.
For a deeper review, focus on understanding each layer's composition, functions of different glands, and recognizing symptoms of common skin