
- 239
- 1 401 497
MAFarooqi
Pakistan
เข้าร่วมเมื่อ 19 มิ.ย. 2012
NCS - 42 - Backstepping control for strict feedback systems
This lecture extends the backstepping control technique to a more general class of nonlinear systems, called strict feedback systems. Some examples and exercise problems are presented to explain the design procedure.
มุมมอง: 1 833
วีดีโอ
NCS - 35 - Chattering in Sliding Mode Control
มุมมอง 1.8Kปีที่แล้ว
Sliding Mode Control is associated with chattering, this lecture explains the chattering phenomenon and its reasons.
NCS - 34c - Sliding Mode Control for Pendulum - Simulation Results
มุมมอง 2.2Kปีที่แล้ว
Simulation result for the designed sliding mode control for the pendulum system are presented in this part of the lecture.
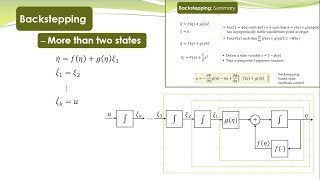
NCS - 41 - Bacstepping Control - General Case - more than two states
มุมมอง 1.6Kปีที่แล้ว
This lecture explains the backstepping control for a more general class of nonlinear systems. Based upon the idea of simple system with only two states, the idea is extended to systems with more than two states. MATLAB/Simulink Simulations are performed to demonstrate the designed controller.
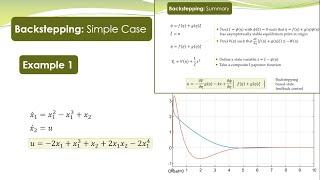
NCS - 40a - Backstepping Control - Basic Concept
มุมมอง 4.6Kปีที่แล้ว
Basic concept of the back-stepping control for nonlinear systems is explained in this lecture. Backstepping is a very powerful technique for design of controllers for nonlinear systems. Systems with particular structure, called strict feedback systems, can be handled with this approach. This lecture explains the concept with a simple case when the system has only two states.
NCS - 40b - Backstepping Control - Example
มุมมอง 3.5Kปีที่แล้ว
This lecture demonstrates the application of back-stepping control technique for the design of controller for nonlinear systems. MATLAB/Simulink simulations are performed to demonstrate the efficacy of the controller.
NCS - 37 - Chattering reduction in SMC (Approach 2)
มุมมอง 1Kปีที่แล้ว
This lecture demonstrates that replacing the signum function with high slope saturation function can reduce the chattering associated with sliding mode control.
NCS - 36b - Chattering reduction - MATLAB demonstration
มุมมอง 1Kปีที่แล้ว
MATLAB Simulations for demonstration of first approach for chattering reduction in sliding mode control.
NCS - 36a - Chattering Reduction (Approach 1)
มุมมอง 1.2Kปีที่แล้ว
Sliding Model Control (SMC) is associated with chattering phenomenon. This lecture explains an approach for reduction of chattering in SMC.
NCS - 34d - Sliding Mode Control explained with phase portraits
มุมมอง 1.6Kปีที่แล้ว
NCS - 34d - Sliding Mode Control explained with phase portraits
NCS - 34b - Sliding Mode Control - Example of Pendulum
มุมมอง 3.3Kปีที่แล้ว
This part of the lecture demonstrates the procedure to design sliding mode control with the help of a simple system of pendulum.
NCS - 34a - Sliding Mode Control - Basic Concept
มุมมอง 12Kปีที่แล้ว
This lecture discusses the concept of Sliding Mode Control (SMC), which is a powerful technique for designing controllers for nonlinear systems. It explains how the control law can bring any initial condition to the sliding surface and maintain trajectories on the surface, leading to stable system dynamics. The approach is robust against uncertainties and can be implemented with a simple contro...
NCS - 19b - Examples: Invariance Set Theorem
มุมมอง 1.1Kปีที่แล้ว
NCS - 19b - Examples: Invariance Set Theorem
NCS - 19a - LaSalle's Invariance Set Theorem
มุมมอง 1.7Kปีที่แล้ว
NCS - 19a - LaSalle's Invariance Set Theorem
NCS - 18b - Krasovskii's Method for Stability
มุมมอง 3.3Kปีที่แล้ว
NCS - 18b - Krasovskii's Method for Stability
NCS - 18a - Selection of Candidate Lyapunov Function
มุมมอง 3.1Kปีที่แล้ว
NCS - 18a - Selection of Candidate Lyapunov Function
NCS - 17b - Examples of Global Asymptotic Stability
มุมมอง 2.3Kปีที่แล้ว
NCS - 17b - Examples of Global Asymptotic Stability
NCS - 17a - Global Asymptotic Stability - Lyapunov Theorem
มุมมอง 2.6Kปีที่แล้ว
NCS - 17a - Global Asymptotic Stability - Lyapunov Theorem
NCS - 16b - Examples: Application of Lyapunov Stability Theorem
มุมมอง 4Kปีที่แล้ว
NCS - 16b - Examples: Application of Lyapunov Stability Theorem
NCS - 16a - Lyapunov Stability Theorem, Energy Concept, Definiteness of functions
มุมมอง 4.4Kปีที่แล้ว
NCS - 16a - Lyapunov Stability Theorem, Energy Concept, Definiteness of functions
LCS - 53c - Diagonal canonical form (DCF) representation of state equations
มุมมอง 15K2 ปีที่แล้ว
LCS - 53c - Diagonal canonical form (DCF) representation of state equations
LCS - 53b - Observable Canonical Form (OCF) and signal flow graphs
มุมมอง 18K2 ปีที่แล้ว
LCS - 53b - Observable Canonical Form (OCF) and signal flow graphs
LCS - 53a - Controllable Canonical Form (CCF) state-space models
มุมมอง 23K2 ปีที่แล้ว
LCS - 53a - Controllable Canonical Form (CCF) state-space models
LCS - 52b - Signal flow graphs for state-space models
มุมมอง 9K2 ปีที่แล้ว
LCS - 52b - Signal flow graphs for state-space models
LCS - 52a - State-space to transfer function
มุมมอง 17K2 ปีที่แล้ว
LCS - 52a - State-space to transfer function
LCS - 51 - Differential equation to state-space, transfer function to state-space, block diagrams
มุมมอง 7K2 ปีที่แล้ว
LCS - 51 - Differential equation to state-space, transfer function to state-space, block diagrams
NCS - 30 - Two more examples of input-output linearization
มุมมอง 2.6K2 ปีที่แล้ว
NCS - 30 - Two more examples of input-output linearization
LCS - 50 - State variables and state equations
มุมมอง 3K2 ปีที่แล้ว
LCS - 50 - State variables and state equations
NCS - 32 - Stabilization and tracking problem using feedback linearization
มุมมอง 2.5K2 ปีที่แล้ว
NCS - 32 - Stabilization and tracking problem using feedback linearization
NCS - 29 - Internal dynamics, zero dynamics, and example of input-output linearization
มุมมอง 4.2K2 ปีที่แล้ว
NCS - 29 - Internal dynamics, zero dynamics, and example of input-output linearization







Thank You So Much Sir
Please explain 16 mark’s questions
السلام عليكم how can we get the full slides for FBL
drive.google.com/drive/folders/1KlLqvsKJ8VALBHYEs3HZB_UuYcSvGJs2?usp=drive_link
Wow! Exactly what I was looking for. Not just solved tutorials, but concrete examples with visual explanations. Very nice video, I give hands sir.
you are the best , I wish all the beast for you, May Allah reward you for this work.
For synchronous motor phasor diagram
9:40 both of them needs to be CCW I think sir.
I really appreciate how you explain why we're taking the derivative and relate it to how the gain is changing. Thank you for making these videos :)
Sir, you have saved my final exam singlehandedly. I am eternally grateful to you
where are u from😊
How did you determine the direction of magnetic flux density Bs due to armature current? WHich rule is that(which equation also)? can i do it using flemings left hand rule? But it shows the direction in the opposite.
awsome thank you sir
You are truly a great teacher. You teach these points verry correctly and to the point. Thanks
Hello sir, thank you so much for the explanation. can you please share the textbook from which you quoted theorem 13.2 ?
Nonlinear Systems by Hassan Khalil.
Please close the Ads Some of them contain haram content
The ads that play on TH-cam videos or Shorts you watch are tailored to your interests. They're based on your Google Ad Settings, the content you've watched, and whether you're signed in or not. support.google.com/youtube/answer/3181017?hl=en#:~:text=The%20ads%20that%20play%20on,news%2C%20updates%2C%20and%20tips.
From where these lectures have been prepared?
Nonlinear Systems by Hassan Khalil, 3rd Edition
Yes farooqi
At 12:54 where θ2(t) ..Wouldn't it effect?
Taking your lectures after 8 years,❤
Thank you very much, Sir.
جزاكم الله خيرا
Thanks for the video, it was a really good example!
جزاكم الله خيرا
thank you for amazing presentation. i have a problem with what you said in 4:50. if sinx1=0 then x1=0 is not the only result. x1=3.1416... can be another result...
You are right. Therefore, the mentioned results will be applicable in the domain where |x1|<pi. Furthermore, the selected Lyapunov function is also valid in that domain.
are the equations same or different for synchronous motor?
There is a slight difference, because the direction of current in generators is opposite to the direction of current in motors.
I love you <3
so if we have x1_dot = f(x1) + x2 and x2_dot = u, we can design backstepping controller. But do you know how to find solution for the model with disturbances: x1_dot = f(x1) + x2 + d1 and x2_dot = u + d2 ? Please let me know.
I believe robustness against d1 can be achieved through effective control design, but I'm uncertain how to address d2. Please share any insights you might have on handling d2.
Thank you, sir, for explaining so well
I have been reading this for more than 3 hours without understanding, u really make it easy.
Thank you sir.
Sir, Is there a chance to share the matlab simulink files? I could not transfer what was explained in the video to Matlab Simulink program.
Wow! Superb Teaching. Thank You
excellent lecture
2024 IMRAN KHAN PROTEST DAYS AND THIS LECTURES HITTING BANGERS.
Why do we get 2e for a very short period of time? All in all very detailed and accurate video on the topic which is very rare. Thank you
There is a brief time during which only two conductors (out of 4) are under pole faces. During this time voltage is 2e.
very simple and crystal clear understanding
Hello can i ask you if this course is fir math students ir engennerinf ?
Assalam o alaikum Sir your lectures are very helpful in understanding the control systems. It is an humble request to please resume the lecture series so that students like me would be able to understand this particular course. Jazakallah u khair.
Thank you so much for the explanation. But you said when omega tends to infinity the real part becomes -3. But omega is in the denominator. This makes the whole denominator very large as compared to the numerator(-3). And this make the real part become zero. And that means the green curve wouldn't be correct. Can you please look into this. Thanks once again.
The real part becomes -3 when omega tends to zero, as depicted in the diagram.
found treasure :0
Thank you sir ❤
17:43 why polarities are from - to + , it goes over it, shouldn't it be from + to - from high potential to low sir?
Voltages are induced in the coils, making them function as voltage sources, and in a voltage source, the direction of current is from - to +
@@MAFarooqi Yes sir I got it thanks a lot...
Thanks a lot sir. Very beneficial source for understanding the concept.
You are God send. Thank you so much
Can you please explain the other compound & series
At 15:07, V3(x) is positive semidefinite since V(x) = 0 for x = [pi,pi] ≠ 0
Yes, you are right. In addition to that, this function is locally positive definite (in a domain |x| < \pi ), therefore, this fuction can be utilized to study local stability of a nonlinear system.
For exponential stability, lambda should be a positive integer instead of a positive number, right? Because lambda = 0.01 is greater than 0 but decays slower than 1/(1+t) ...
Lambda needs not to be necessarly an integer, it can be any positive REAL number.
VERY HELPFUL, SANA MAKAPASA KAMI SA BASIC NA TOPIC NA I2 HUHU
Thank you sir ❤
Thank you sir❤